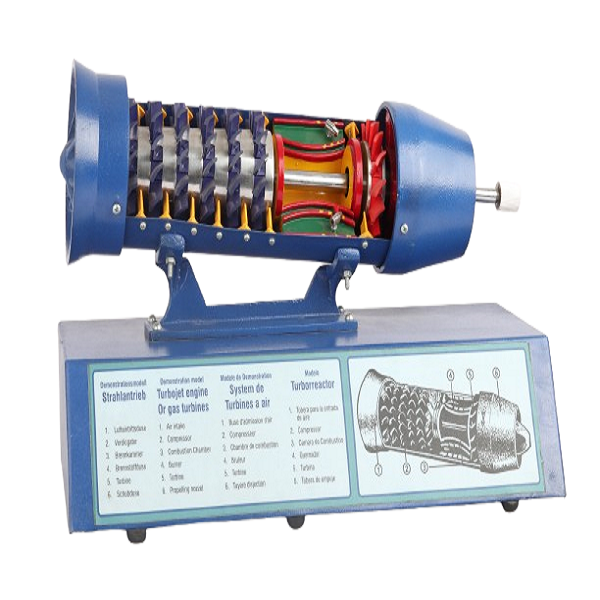
A turbojet engine works by compressing air, mixing it with fuel, burning the mixture, and then using the hot exhaust gases to generate thrust:
-
1. Air intakeAir is drawn into the engine through the inlet. The inlet’s design is important for directing airflow efficiently while minimizing drag and shock waves.
-
2. CompressionThe air is compressed by the compressor, which increases its pressure and temperature.
-
3. Fuel injectionFuel is added to the combustion chamber and mixed with the compressed air.
-
4. CombustionThe fuel and air mixture is ignited and burned at a temperature of over 2,000 degrees Celsius.
-
5. TurbineThe exhaust gases pass through the turbine, which extracts energy to power the compressor.
-
6. NozzleThe exhaust gases are expanded in the nozzle, which accelerates them to a high velocity to generate thrust.
The thrust of a turbojet engine can be increased by adding an afterburner, which injects more fuel into the hot exhaust gases to increase their temperature and exit velocity.
Turbojet engines have a relatively simple design, take up little space, and are capable of very high speeds.





There are no reviews yet.